
Specification
Product name Monoclonal mouse anti-human S100B
Name on the label S100B Ab
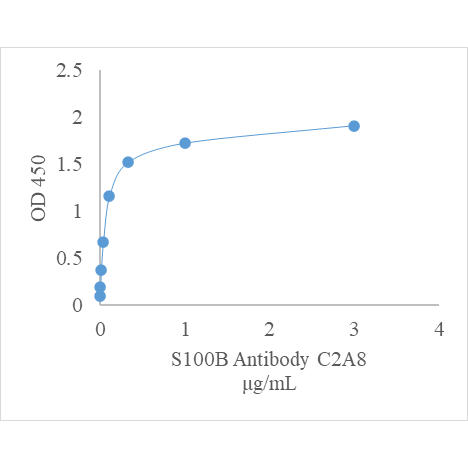
Clone number C2A8
Description Hybridoma clone derived from hybridization of Sp2/0 myeloma cells with spleen cells of Balb/c mice.
Immunogen Recombinant human S100B (1-92aa.) protein.
Source/Isotype Mouse, IgG1 Kappa
Reactivity Human
Specificity Human S100B
Epitope Human S100B
Purification Protein G chromatography
Application ELISA, others unspecified.
Form Liquid
Storage Buffer In 1?PBS, pH 7.4
Storage Instruction Shipped at 4°C. Store at +4°C short term (1-2 weeks). Store at -20°C or lower long term. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
Shipping condition With gel ice, gry ice allowed.
UniProt ID P04271
Entrez-Gene Id 6285
Protein Name Protein S100-B
Gene Name S100B
S100B, previously called S100 beta, belongs to the S100 family within the EF-hand superfamily of Ca2+ binding proteins. S100 proteins contain two EF-hand motifs that differ in affinity, separated by a hinge region with a hydrophobic cleft that is exposed upon Ca2+ binding. S100B is a 91 amino acid (aa) protein, after removal of the initial methionine, and is found as homodimers of 10.4 kDa monomers. Human S100B shares 99%, 98%, 100%, 99% and 97% aa sequence identity with mouse, rat, rabbit, equine and bovine S100B, respectively. Within the S100 family, human S100B shows the highest aa identity (59%) with S100A1. S100B is expressed primarily by astrocytes and oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system, and by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. Ca2+-bound S100B interacts in vitro with at least 20 cytoplasmic proteins, including several structural molecules such as tubulin and GFAP. It can inhibit the phosphorylation of these kinase substrates and others such as tau and neuromodulin. Astrocytes can secrete S100B, which then acts in a cytokine-like manner. Nanomolar concentrations of S100B are secreted constitutively, promote proliferation, and are neurotrophic and anti-apoptotic. Blood levels of S100B reflect extracellular concentrations within the nervous system, and are elevated in Down’s syndrome, Alzheimer’s disease and Tourette’s syndrome, metabolic stress, acute brain injury and brain tumors. Micromolar concentrations of S100B can be destructive and pro-apoptotic; they induce the expression of iNOS, COX-2, IL-1, IL?6 and TNF-alpha by microglia, astrocytes or neurons. Most extracellular actions of S100B can be mediated by RAGE (receptor for advanced glycation end products), which is also a receptor for other S100 proteins.
Clone number Cat. Description
C2A8 RXS007Ab26-0001 Monoclonal mouse anti-human S100B
C3B8 RXS007Ab27-0001 Monoclonal mouse anti-human S100B
D6B2 RXS007Ab06-0001 Monoclonal mouse anti-human S100A1















 加入購物車
加入購物車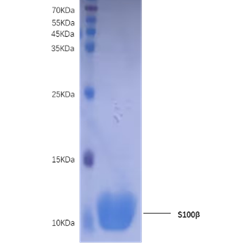







 13632887203
13632887203